POPULAR ARTICLES
- e-Invoicing in France 2026: Timeline, Requirements, Guidelines & Format
- What is a PDP, OD and PPF in France e-Invoicing?
- All About e-Reporting under France e-Invoicing
- VAT in France 2026: Rates, Registration, Filing, Payments & Penalties
- France e-Invoicing and e-Reporting FAQs: Rules, Scope & 2026 Requirements
- Credit Note in France: Meaning, Usage, Example & Template
- Factur-X in France: What It Is, How It Works and Steps to Generate
- SIREN and SIRET Numbers: How to Apply and Where to Get Them
- Common e-Invoicing Mistakes in France & How to Avoid Them
- XML vs PDF/A-3 in e-Invoicing: Handling Structured & Unstructured Data
- Top 7 Misconceptions About E-Invoicing in France for 2026
- What is the EN 16931 Electronic Invoicing Standard in France?
- Handling Structured & Unstructured Data in e-Invoicing: XML and PDF/A-3 Explained
YOU MIGHT BE INTERESTED IN
e-Invoicing in France 2026: Timeline, Requirements, Guidelines & Format
Starting September 1, 2026, e-invoicing in France becomes mandatory for all VAT registered businesses. Companies must use approved digital invoice formats and certified platforms, replacing paper and standard PDF invoices.
Key Takeaways: France e-Invoicing Requirements
- All French VAT registered businesses must receive e-invoices from September 1, 2026.
- Large and medium companies must issue e-invoices from September 1, 2026; small and micro-enterprises from September 1, 2027.
- E-invoices must use approved digital formats: Factur-X, UBL, or CII and be sent and received through certified Partner Dematerialization Platforms (PDPs).
- Traditional paper and standard PDF invoices are not allowed for B2B; only structured electronic invoices are valid.
- E-reporting is required for B2C, cross-border, and other non-B2B transactions.
What is e-invoicing in France?
e-Invoicing in France is the legal requirement for businesses to issue, send, and receive invoices in a structured electronic format, using approved digital standards and certified platforms so that invoice data can be automatically processed and reported to the French tax authorities for greater efficiency, transparency, and fraud prevention.
Article 153 of 2020 of French Finance Law mandates B2B e-invoicing mandatory for all businesses registered under France Value Added Tax (VAT).
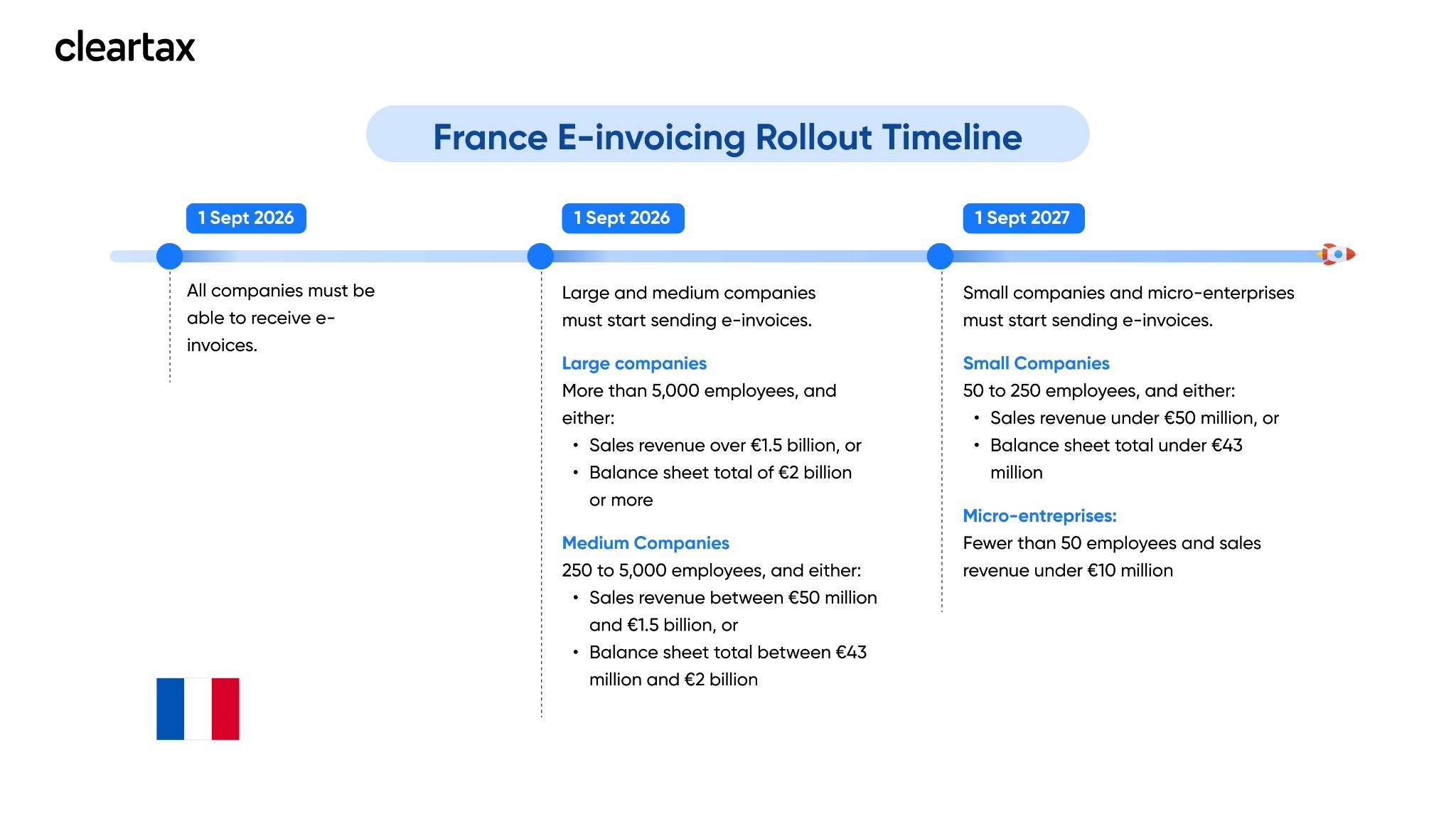
France e-Invoicing and e-Reporting Mandate Deadlines
The French government has postponed the original e-invoicing rollout, which was previously set for July 1, 2024. This delay allows for a smoother transition and ensures that all stakeholders have adequate time to prepare for this significant reform. The new implementation dates and criteria are now confirmed and detailed in the latest Finance Law.
Notes:
- All businesses in France must be able to receive e-invoices by September 1, 2026.
- Company size is determined based on the number of employees and financial thresholds, as defined by the French government.
- The evaluation is typically based on the figures from the previous financial year. If a company exceeds more than one threshold at the end of the financial year, it is immediately classified in the higher category for the following year.
- The French government may grant up to a three-month extension for each phase if needed.
France 2026 E-Invoicing Compliance Roadmap (PDF): A detailed implementation roadmap outlining regulatory scope, platform architecture, reporting flows, controls, and recommended sequencing toward go-live.
What is e-Reporting in France?
e-Reporting in France refers to the electronic transmission of specific transactional and payment data to the French tax authorities for certain operations that are not covered by the mandatory B2B e-invoicing regime.
Who Must Perform e-Reporting?
- French Businesses: All businesses established in France must e-report transactions that are outside the scope of mandatory e-invoicing.
- Foreign Companies: Foreign companies that are VAT registered in France but do not have a permanent establishment are also required to perform e-reporting for their relevant transactions.
Who must comply with e-Reporting Obligations?
According to the French tax administration, the following transactions must be e-reported:
- Business-to-Consumer (B2C) Transactions: Sales of goods or services by French businesses directly to end consumers (not subject to B2B e-invoicing).
- Exports: Supplies of goods and services from France to countries outside the European Union.
- Imports: Purchases of goods and services by French businesses from countries outside the European Union.
- Intra-Community EU Dispatches: Sales of goods and services from France to other EU member states (intra-community supplies).
- Intra-Community EU Acquisitions: Purchases of goods and services by French businesses from other EU member states (intra-community acquisitions).
How is e-Reporting Performed?
e-Reporting is carried out via certified Partner Dematerialization Platforms (PDPs) or Dematerializing Operators (ODs), which transmit the required data to the tax authorities. The data to be reported includes key invoice details, transaction amounts, VAT information, and payment status, depending on the transaction type.
e-Reporting must be performed within specific deadlines set by the French tax administration, typically in real-time or at regular intervals.
e-Invoicing vs e-Reporting: What’s the Difference?
e-Invoicing replaces traditional B2B invoicing with real-time structured invoice exchange, while e-reporting provides tax authority visibility into transactions outside the e-invoicing scope.
Here are the major differences
Aspect | E-Invoicing | E-Reporting |
Scope | Domestic B2B transactions (both parties VAT-registered in France) | Transactions outside e-invoicing scope: B2C, cross-border B2B, exports |
Transaction Types | Business-to-business sales between French entities | B2C sales, international B2B (EU & non-EU), exports |
Invoice Format | Mandatory structured formats: UBL 2.1, UN/CEFACT CII, or Factur-X | Any format for customer invoice; structured data to tax authority |
Data Detail Level | Complete invoice detail: all line items, full party info, VAT breakdown | Summary/aggregate data only (daily totals for B2C by SIREN) |
Recipients | Buyer + French tax authority (dual transmission) | French tax authority only (single transmission) |
Submission Timing | Real-time/immediate upon invoice creation | Periodic: every 10 days for transactions, monthly for payments |
Lifecycle Tracking | Yes - tracks: sent, received, rejected, accepted, paid, collected | No - no status tracking required |
Primary Purpose | Replace traditional invoicing; enable automated VAT reporting | Provide tax authority visibility into non-e-invoiced transactions |
Platform Use | Mandatory use of certified Approved Platforms (PA) | Via Approved Platforms or PPF; more flexible than e-invoicing |
Implementation Date | September 1, 2026 (large/medium); Sept 1, 2027 (small/micro) | September 1, 2026 (large/medium); Sept 1, 2027 (small/micro) |
Why is e-invoicing being introduced in France?
The French Government is committed to the implementation of e-invoicing for businesses. This reform aims to:
- Strengthen their competitiveness due to the reduction of the administrative burden and the productivity gains resulting from dematerialisation.
- Simplify their reporting obligations by pre-filling in VAT returns.
- To curb fraud cases and benefit the genuine businesses
- Improve real-time knowledge of the business activity.
French e-Invoicing Model and Framework
France has adopted the sophisticated and evolving 5-corner model for electronic invoicing and e-reporting, aiming to modernize business processes, reduce VAT fraud, and streamline tax reporting. The system has transitioned from a hybrid "Y-model" to a more decentralized model, placing certified private platforms (PDPs) at the middle of invoice exchange and compliance.
5-Corner Model (Y-Model): Structure and Key Elements
France planned a hybrid system (the "Y-model") where businesses could exchange invoices via the public portal (PPF), certified private platforms (PDPs), or dematerialization operators (ODs). The PPF played a central role in this model.
As of late 2024, France shifted to a pure 5-corner model. Now, all e-invoice exchanges must go through certified PDPs, which are responsible for both invoice transmission and e-reporting to the tax authority. The PPF now acts only as a directory and data hub, not as an exchange platform.
Authorized Formats
- Factur-X (hybrid XML/PDF)
- UBL 2.0/2.1 (Universal Business Language)
- CII (Cross Industry Invoice)
- PeppolBIS
- EDIFACT
Key Participants in French e-Invoicing
The French e-invoicing system brings together several key participants, each playing a crucial role in ensuring that invoices are created, transmitted, received, and reported in a secure and compliant manner. This collaborative framework streamlines business transactions, improves tax compliance, and supports the automation of VAT reporting.
Participant | Role and Function |
Supplier (Seller) | Creates invoices in approved electronic formats and initiates the invoicing process via a certified PDP. |
Buyer (Customer) | Receives invoices through their chosen PDP, processes, pays, and manages any disputes or corrections. |
PDP (Partner Dematerialization Platform) | Validates invoice format, ensures compliance, converts formats if needed, routes invoices, and reports data to the PPF. |
PPF (Public Invoicing Platform) | Maintains the central directory, aggregates invoice and reporting data, and forwards information to the tax authority. |
DGFIP (French Tax Authority) | Oversees the e-invoicing mandate, monitors compliance, and uses data for VAT control and enforcement. |
OD (Dematerialization Operator) | Assists with format conversion and e-reporting for transmission but doesn’t transmit it themselves |
e-Invoicing Process in France
The French e-invoicing process is designed for efficiency, security, and transparency, using standardized formats and certified platforms for all B2B transactions.
- Invoice Generation: The supplier creates an invoice in an approved structured format (Factur-X, UBL, or CII). If the supplier’s system cannot generate the required format, a certified platform (PDP) or a dematerialization operator (OD) can convert the invoice into the correct format.
- Transmission via PDP: The supplier sends the e-invoice to their chosen certified Partner Dematerialization Platform (PDP). The PDP checks the invoice for correct format and compliance with business rules.
- Interoperability and Delivery: If the buyer uses a different PDP, the supplier’s PDP forwards the invoice to the buyer’s PDP, ensuring seamless delivery. The buyer receives the invoice in their preferred structured format through their PDP.
- E-Reporting: The PDP extracts required invoice data and, if needed, payment status, then sends this information to the public platform (PPF) for tax reporting. For transactions not covered by e-invoicing (such as B2C or cross-border sales), PDPs or ODs handle e-reporting directly to the PPF.
- Tax Authority Processing: The PPF aggregates all received data and forwards it to the French tax authority (DGFIP) for compliance checks and VAT control.
What are the Requirements for e-Invoicing in France?
To comply with France’s mandatory e-invoicing and e-reporting framework, businesses must meet the following requirements:
- Digital Format: Invoices must be created and processed in specific electronic formats (such as Factur-X, UBL, or CII) that allow for automated data handling.
- Certified Platforms: All invoices must be sent and received through government approved electronic invoicing platforms called Partner Dematerialization Platforms (PDPs).
- Real-Time Reporting: Invoice data is automatically shared with French tax authorities, allowing for better monitoring and compliance.
- E-Reporting for Other Transactions: For transactions that don’t require e-invoicing (like sales to consumers or cross-border deals), key transaction details must still be reported electronically.
- No More Simple PDFs or Paper: Traditional paper invoices or regular PDF files sent by email are no longer allowed unless they are converted into the approved digital formats and processed through a certified platform.
How Should Businesses Prepare for France e-Invoice Mandate
To successfully transition to France e-invoice mandate, businesses should take a strategic and organized approach:
1. Build an Internal Task Force: Create a cross-functional team that includes management, accounting, and IT staff. This group will oversee the transition, coordinate between departments, and ensure everyone understands the new requirements.
2. Audit Current Processes: Review your existing invoicing, accounting, and ERP workflows. Identify which parts are already digital and where changes or upgrades are needed to comply with the new e-invoicing standards.
3. Assess Technical Readiness: Check if your current systems can generate invoices in the required electronic formats (such as Factur-X, UBL, or CII). If not, plan for necessary software updates or integrations.
4. Choose a Certified PDP: Research and select a certified Partner Dematerialization Platform (PDP) that matches your business needs. The PDP will handle the sending, receiving, and reporting of your invoices.
5. Train Staff and Communicate: Educate all relevant employees about the new e-invoicing workflows and compliance requirements. Make sure they know how to use the chosen PDP and any updated digital tools.
6. Test and Integrate Systems: Run tests with your selected PDP to ensure that invoices are correctly formatted, transmitted, and reported. Address any technical or procedural issues before the system goes live.
What are the benefits of e-invoicing in France?
Here are a few benefits of e-invoicing in France:
- Enhanced data sharing
- Increased productivity due to faster processing times
- Optimised cash flow with shorter payment times
- Increased visibility of all processes & performance
- Lowered operating costs
- Easy preparation of VAT returns
- Reduced VAT frauds
- Better supplier relationships
Penalties for non-compliance with France e-invoicing
Failure to comply with France’s e-invoicing and e-reporting requirements can result in significant financial penalties. Penalties apply to both businesses and certified Partner Dematerialization Platforms (PDPs), with higher thresholds for PDPs due to their critical role in the system.
Non-Compliance Type | Penalty per Instance | Maximum Penalty (per year) |
Failure to issue an e-invoice | €15 per invoice | €15,000 (per business) |
Failure to transmit e-reporting data | €250 per transmission | €45,000 (per business) |
Failure by PDP to transmit/receive invoice | €15 per invoice | €45,000 (per PDP) |
Missing or inaccurate invoice information | €15 per error (capped at 25% of invoice value) | - |
Issuing fraudulent invoices | 50% of the invoice amount | €375,000 (per business) |
Failure to issue any invoice | Up to €75,000 (individuals); €375,000 (businesses); repeat offenses: €750,000 | - |
Additional Notes:
- Penalties apply separately to e-invoicing and e-reporting failures.
- The penalty for missing or inaccurate invoice information is limited to a maximum of 25% of the invoice value.
- Fraudulent invoicing attracts the highest penalties, reflecting the seriousness of tax evasion.
- Penalties are cumulative and can be imposed in addition to other administrative or criminal sanctions.
- For PDPs, the annual cap is higher due to their systemic importance.
How ClearTax Can Help with e-Invoicing Implementation in France
ClearTax is a pre-approved Plateforme Agréée (PA) ensures compliance with France’s 2026 e-invoicing mandate, meeting all PA requirements for security and interoperability.
- Connect effortlessly with any ERP or POS system via APIs.
- Compliant e-invoice exchange with the French Public Portal (PPF).
- Manage e-invoicing and compliance from a single secure dashboard.
- Automatic updates to stay compliant with French regulations.
- 99.99% uptime for uninterrupted invoicing.
- Advanced validation for faster, error-free processing.
- Instant alerts for invoice status changes.
- Automated updates to improve vendor and customer interactions.
Invoice Lifecycle Status Management in France
France’s e-invoicing mandate introduces mandatory, real-time lifecycle status tracking for every invoice, transforming invoices from static documents into dynamic digital records. Through standardized status messages, from creation and submission to approval, rejection, payment, and archival to businesses, platforms, and the French tax authority (DGFiP) gain continuous visibility into each transaction.
The system includes 14 possible statuses (with four mandatory: Submitted, Refused, Payment Sent, Payment Received) and uses automated, real-time CDAR messages to ensure transparency, prevent fraud, and support VAT compliance.
This requirement is a core part of France’s B2B e-invoicing reform, creating a complete digital audit trail and aligning finance, ERP, and payment workflows with strict regulatory expectations.
Conclusion
B2B e-invoicing in France begins September 2026, requiring all VAT registered businesses to receive structured e-invoices, with large and mid-sized companies also issuing them from this date, and small and micro-enterprises following in September 2027. All invoices must flow through certified Partner Dematerialization Platforms (PDPs), while the PPF now acts only as a directory and tax data hub. Compliance requires using approved formats such as UBL 2.1, CII, or Factur-X, with PDFs allowed only until the end of 2027. The mandate also introduces e-reporting for B2C and cross-border transactions. Real-time data exchange enables tax authorities to monitor VAT activity and enforce strict penalties for non-compliance.


