POPULAR ARTICLES
- VAT in UAE: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
- How to file the VAT return in UAE: Detailed Step-By-Step Guide
- VAT Invoicing in UAE
- Excise Tax in the UAE: Rate, Exemption and Calculation
- Zero Rated vs. Exempted VAT Supplies in UAE: A Complete Guide
- MoFA Attestation in UAE: Requirements & How to Attest Documents From MoFA?
RELATED ARTICLES
- e-Invoicing in United Arab Emirates (UAE): A Complete Guide For Your Business
- What is the Peppol CTC Model in UAE for E-Invoicing?
- UAE e-Invoicing Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- UAE Tax Credit Note: Examples, Formats & Benefits
- Digital Signature Certificate in UAE: Benefits, Process & How It Works
- VAT Invoicing in UAE
- VAT Rate List in UAE
- How to Claim VAT Refund in UAE?
- What are the Penalties for Non-Compliance under the UAE VAT?
- TRN Verification in UAE: Step-by-Step Process to Verify VAT Number in UAE
- Excise Registration in UAE: A Comprehensive Guide
e-Invoicing in UAE: Key Requirements, Implementation Timeline & Latest Updates
The UAE has announced a phased rollout of mandatory e-invoicing under its new Electronic Invoicing System (EIS), beginning with a pilot in July 2026 and full implementation for VAT registered businesses in stages from 2027 onward.
Key Takeaways on UAE e-Invoicing
- e-Invoicing in UAE applies to all VAT-registered entities for B2B and B2G transactions, excluding B2C and certain exempt sectors.
- Large businesses with revenue ≥ AED 50 million must appoint an ASP by 31 July 2026 and implement mandatory e-invoicing from 1 January 2027.
- Only machine-readable formats (XML/JSON using UBL or PINT) are valid; paper or PDFs won’t qualify.
- Accredited Service Providers (ASPs) are mandatory for transmitting, validating, and storing invoices.
- Federal Tax Authority (FTA) will monitor, regulate, and store all e-invoices for compliance.
What is e-Invoicing in UAE?
E-invoicing in the UAE refers to the electronic creation, exchange, and storage of invoices in a structured digital format under the government’s new Electronic Invoicing System (EIS). This move is part of the UAE’s wider strategy to digitize tax administration, enhance VAT compliance, and align with international best practices.
Unlike traditional paper or PDF invoices, a valid UAE e-invoice must:
- Be issued in structured digital formats such as XML or JSON using standards like UBL or PINT.
- Be transmitted through an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) using the Peppol-based DCTCE model (5-corner model).
- Be reported and stored within the Federal Tax Authority’s (FTA) e-Billing System for monitoring and compliance.
- Exclude manually created or unstructured formats (PDFs, JPGs, or paper invoices), which will not qualify as valid e-invoices.
e-Invoicing Implementation Timeline
The UAE government has released updated regulations through Ministerial Decision No. 243 of 2025 and Ministerial Decision No. 244 of 2025 on 28th September, which officially set out the phased rollout of the Electronic Invoicing System.
The new implementation roadmap is as follows:
Phase | Category | Deadline to Appoint ASP | Mandatory Implementation Date |
Pilot Programme | Selected businesses (Taxpayer Working Group) | Not Applicable | 1 July 2026 |
Voluntary Adoption | Any business (optional) | Flexible | From 1 July 2026 |
Phase 1 | Large businesses with revenue ≥ AED 50 million | 31 July 2026 | 1 January 2027 |
Phase 2 | Businesses with revenue < AED 50 million | 31 March 2027 | 1 July 2027 |
Phase 3 | All UAE Government Entities | 31 March 2027 | 1 October 2027 |
e-Invoicing Requirements in UAE
To comply with the UAE’s new e-invoicing system, businesses must follow these key requirements:
- Digital Format Only: Invoices must be created in XML or JSON formats (PDFs or paper invoices are not valid).
- Structured Standards: Use recognized standards like UBL (Universal Business Language) or PINT (Peppol Invoice Standard).
- Transmission Through ASP: All invoices must be sent and received via an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) approved by the Ministry of Finance.
- Real-Time Submission: Invoices and credit notes must be transmitted through the system within 14 days of the transaction.
- Mandatory Data Fields: Invoices must include all fields prescribed by the Ministry of Finance (seller details, VAT number, tax breakdown, etc.) in the Data Dictionary.
- Digital Credit Notes: Credit notes must also be issued electronically in the same format and system as invoices.
- Data Storage in UAE: All invoice and credit note data must be stored within the UAE, in line with the Tax Procedures Law.
- System Failures: Any technical failure must be reported to the FTA within 2 business days, using the process it defines.
e-Invoicing Process in UAE
To comply with the UAE’s e-Invoicing mandate, businesses will need to follow a structured process supported by their ERP systems and Accredited Service Providers (ASPs). Here’s how it works in practice:
- Hire an Accredited Service Provider (ASP): Businesses must appoint an FTA-accredited ASP. The ASP works with your technical/ERP team to customize your ERP so that it can capture all relevant invoice data fields required by the FTA (often called the “data dictionary”).
- Map ERP Data to Standard Fields: Each e-invoice requires specific information such as seller/buyer details, VAT registration number, item description, taxable amount, VAT rate, total invoice value, etc. The ASP ensures your ERP is aligned with this data dictionary and maps the captured fields correctly.
- Convert to Required Format: Once details are entered in your ERP, the ASP’s core system converts the invoice into the mandatory digital format (XML or JSON) using approved standards like UBL or Peppol PINT.
- Validate and Enrich: Before sending, the ASP validates the data, corrects errors if any, and enriches the invoice with missing mandatory fields (such as standardized codes or unique identifiers) to ensure compliance.
- Real-Time Transmission: The ASP then transmits the invoice simultaneously to
- The FTA’s e-Billing system, for monitoring and compliance.
- The buyer’s ASP, so the recipient receives the invoice in a processable format.
- Secure Storage and Access: Both the issuer and recipient must securely store the e-invoice and related data inside the UAE as per FTA rules. Invoices remain accessible through the ERP or ASP portal for audits, reconciliations, and VAT filings.
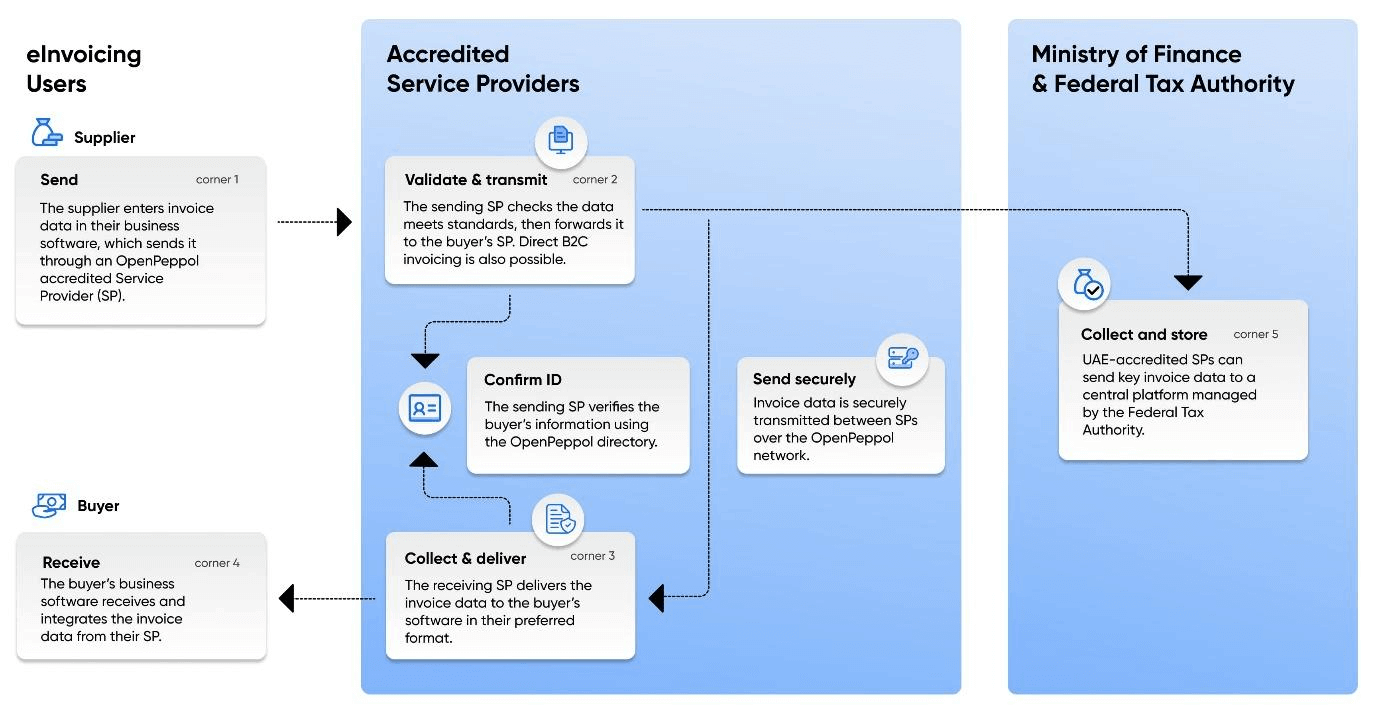
e-Invoicing Framework in UAE
The UAE’s CTC e-invoicing framework, known as the "DCTCE" model, is based on the Peppol "5-corner" model. The "5-corner" model involves five main components:
- Issuer: The party generating the invoice.
- Receiver: The party receiving the invoice.
- E-Billing System by FTA: Integrates with the Peppol PINT (Peppol Invoice Standard) for data exchange. The e-billing platform acts as an invoice repository but does not validate the invoices.
- Sender Accredited Service Provider (ASP): Verifies the data and transmits the invoice to the tax authority and the receiver ASP
- Receiver ASP: Verify the received data and transmit the e-invoice to the purchase party (receiver)
Scope of e-Invoicing in UAE
The scope of e-invoicing in the UAE is defined under Ministerial Decisions No. 243 and 244 of 2025. The Electronic Invoicing System applies broadly to most business transactions carried out in the UAE, with certain exclusions and phased implementation requirements.
- All VAT-registered persons engaged in taxable business transactions are required to issue and exchange electronic invoices and credit notes through the Electronic Invoicing System.
- Both business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-government (B2G) transactions fall under the scope.
e-Invoicing Exemptions in UAE
Certain categories of transactions are excluded from mandatory e-invoicing under Article 4 of Ministerial Decision No. 243/2025:
- B2C transactions are not subject to mandatory e-invoicing
- Transactions conducted by government entities in a sovereign capacity that are not in competition with the private sector.
- International passenger air transport services where electronic tickets are issued.
- Ancillary airline services linked to passenger transport when an Electronic Miscellaneous Document (EMD) is issued.
- International transport of goods by air, where an airway bill is issued. This exclusion applies for a limited period of 24 months from the system’s effective date.
- Financial services that are VAT-exempt or zero-rated.
- Any other transactions determined by the Minister of Finance.
Role of Accredited Service Providers (ASPs) in UAE e-Invoicing
As per UAE regulations, all taxpayers subject to the e-invoicing mandate must appoint an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) prior to implementation deadlines (July 2026: January/October 2027, depending on revenue and entity type). This requirement reflects the UAE’s decision to adopt a Peppol-based Continuous Transaction Control (CTC) model, where ASPs are central to ensuring compliance, accuracy, and secure transmission of e-invoices.
Key Functions of ASPs in UAE e-Invoicing
- Data Mapping: Align invoice data from business ERP/accounting systems to FTA’s required structured formats (XML/JSON using UBL or PINT).
- Validation: Check invoices against UAE’s e-invoicing schema, VAT law requirements, and Peppol standards before submission.
- Data Enrichment: Add missing or required information (such as digital signatures, tax details, identifiers) to ensure compliance.
- Format Conversion & Correction: Convert invoices from internal formats (e.g., PDF, CSV, Excel) into accepted machine-readable formats; correct errors before submission.
- Transmission: Route invoices securely through the Peppol network to the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) and recipient ASP in real time.
- Compliance Reporting: Ensure invoices and credit notes are reported to FTA within statutory deadlines (e.g., 14 days of transaction).
- Security & Authenticity: Apply digital signatures, encryption, and tamper-proofing to maintain integrity and authenticity.
- Integration Support: Provide APIs, middleware, and onboarding support for seamless ERP/business system integration.
- Monitoring & Notifications: Track invoice status, provide real-time alerts for failures, and ensure fallback procedures during system downtime.
- Archival & Storage: Enable secure storage of e-invoices and related data within UAE, as per retention requirements.
Mandatory Fields of an e-Invoice in the UAE
Every e-invoice and e-credit note must include all data fields and particulars prescribed by the Ministry of Finance. These fields follow the UAE e-Invoicing Data Dictionary and align with Peppol/UBL standards.
Category | Mandatory Fields |
Seller (Supplier) Information | Legal name of supplier TRN (Tax Registration Number) Address and contact information ASP identifier or system ID |
Buyer (Recipient) Information | Legal name of buyer TRN (if VAT registered) Address and contact details |
Invoice Metadata | Unique Invoice Number (UUID) Issue Date and Time (in UTC) Invoice Type Code (standard, credit note, or debit note) Currency Code (AED or applicable foreign currency) |
Transaction Details | Description of goods or services Quantity and unit of measure Unit price and total before tax VAT rate and VAT amount per line item Discounts or adjustments (if applicable) |
Tax Summary | Total taxable amount Total VAT amount Gross invoice total (inclusive of VAT) |
Digital and Transmission Details | ASP digital signature and validation stamp Hash or QR code for authenticity Reference to previous invoice (for credit/debit notes) Transmission timestamp and system acknowledgment ID |
Optional / Additional Fields | Purchase order reference number Payment terms and due date Bank details or IBAN Remarks for buyer or FTA audit trail |
UAE e-Invoicing Penalties and Fines (November 2025)
The UAE Ministry of Finance has issued Cabinet Decision No. 106 of 2025, which defines administrative penalties for non-compliance with the UAE Electronic Invoicing System. These penalties apply to issuers and recipients once they are formally mandated to adopt e-invoicing. Businesses using e-invoicing voluntarily before being mandated are not subject to these fines.
Violation | Who it applies to | Penalty amount | How it’s calculated / cap
|
Failure to implement e-invoicing or appoint an Accredited Service Provider (ASP) within the prescribed timeline
| Issuer | AED 5,000 | For each month or part of a month of delay
|
Failure to issue and transmit an electronic invoice through the system on time
| Issuer
| AED 100 per invoice
| Capped at AED 5,000 per calendar month
|
Failure to issue and transmit an electronic credit note through the system on time | Issuer
| AED 100 per credit note | Capped at AED 5,000 per calendar month
|
Failure to notify the Authority of a system failure within the prescribed timeline
| Issuer
| AED 1,000 per day | For each day (or part of a day) of delay
|
Failure to notify the Authority of a system failure within the prescribed timeline
| Recipient
| AED 1,000 per day
| For each day (or part of a day) of delay
|
Failure to inform the appointed ASP of updates to Authority-registered data within the prescribed timeline
| Issuer or Recipient | AED 1,000 per day
| For each day (or part of a day) of delay
|
How to Prepare for e-Invoicing (Effective July 2026)
Businesses must prepare early to ensure their systems and data meet compliance standards. Here is how you can prepare for e-invoicing compliance
1. Understand the Timeline and Scope: The pilot begins in July 2026, with phased enforcement based on business size. Entities earning AED 50 million or more must comply first, followed by smaller VAT-registered businesses and government bodies. B2C-only businesses are excluded until further notice.
2. Appoint an Accredited Service Provider (ASP): All VAT-registered businesses must appoint an FTA-accredited ASP before implementation. The ASP converts invoices into XML or JSON and sends them securely to the Federal Tax Authority and buyers. Complete onboarding before July 2026 and ensure the ASP follows Peppol standards like UBL or PINT.
3. Upgrade ERP and Accounting Systems: ERP systems must create structured invoices in XML or JSON, map all fields to the Ministry’s data dictionary, apply digital signatures, and link directly to the ASP. Manual or PDF invoices will no longer qualify as valid once e-invoicing takes effect.
4. Test During the Pilot Phase: From July to December 2026, businesses should test system integration with the ASP and FTA sandbox. Verify data accuracy, run sample transactions, and train teams on new invoicing and reporting workflows to ensure readiness before full rollout.
5. Establish Data Governance and Storage: E-invoices and credit notes must be stored within the UAE as required by the Tax Procedures Law. Offshore or external hosting is prohibited. Implement secure archiving, access control, and retrieval processes to support audits and compliance.
6. Ensure Compliance and Reporting Readiness: Update VAT workflows for real-time reporting and establish protocols for handling system issues. Any technical failure must be reported to the FTA within two business days. Train staff and budget for ASP integration, digital signatures, and compliance management to ensure a smooth transition.
How ClearTax Can Help Your Business with e-Invoicing in UAE?
ClearTax is a pre-approved FTA and MoF-compliant Accredited Service Provider(ASP) that can help your business comply with the UAE’s e-invoicing requirements. ClearTax offers a Peppol-ready solution that seamlessly integrates your business system with the FTA portal, ensuring secure and compliant transmission of invoice data.
Here’s how ClearTax can assist:
- Integration with the FTA Portal: ClearTax integrates your business system with the FTA’s e-billing system, ensuring that e-invoices are submitted in real-time, using the specified formats like XML or JSON.
- Peppol-Ready: ClearTax follows the Peppol specifications for data exchange, ensuring compliance with the UAE’s Continuous Transaction Controls (CTC) model.
- End-to-End E-Invoicing Solution: ClearTax provides a complete solution for issuing, submitting, and receiving e-invoices. It tracks the status of submitted invoices sends email notification for e-invoices.
- Web-Based Portal: ClearTax offers a user-friendly web-based portal that allows you to manage the entire e-invoicing process in one place, from generating invoices to tracking their submission and status.
- 100% E-Invoicing Compliance: With ClearTax, your business can achieve 100% compliance with the UAE’s e-invoicing regulations.
Conclusion
The UAE is advancing its tax digitization agenda with the introduction of mandatory e-invoicing through the Electronic Invoicing System (EIS). Set to begin with a pilot in July 2026, the system will be rolled out in stages starting 2027, initially targeting large businesses before expanding to all VAT-registered entities for B2B and B2G transactions.
Accredited Service Providers (ASPs) will play a central role in transmitting and validating invoices through the FTA’s e-Billing platform, ensuring compliance, authenticity, and secure storage within the UAE. With strict compliance measures and penalties for violations, businesses are urged to begin preparations early, upgrading ERP systems and aligning operations with the new requirements.
UAE Government E-Invoicing Resources
References | Details |
Central hub for UAE e‑invoicing updates and documents | |
Official FAQs on scope, rules, and processes | |
How ASPs apply and eligibility criteria | |
Repository of ministerial decisions and tax laws | |
FTA’s platform for tax services and filings | |
Official VAT guides and reference materials | |
Government overview of digital invoicing | |
Establishes scope, duties, exclusions, ASP appointment | |
Phased rollout timeline and key deadlines | |
Technical framework and data dictionary detail |



