E-Invoicing in Germany: Obligations, Timeline, Requirements, Format & Examples
Germany has announced mandatory e-invoicing requiring all VAT-registered businesses to issue structured, machine-readable electronic invoices for domestic B2B sales. This reform standardizes invoice formats, enhances tax compliance, and gradually phases out traditional paper and PDF invoices for most business dealings.
Key Takeaways: e-Invoicing Requirements in Germany
- e-invoices must use structured formats like XRechnung or ZUGFeRD 2.1+, enabling automated processing.
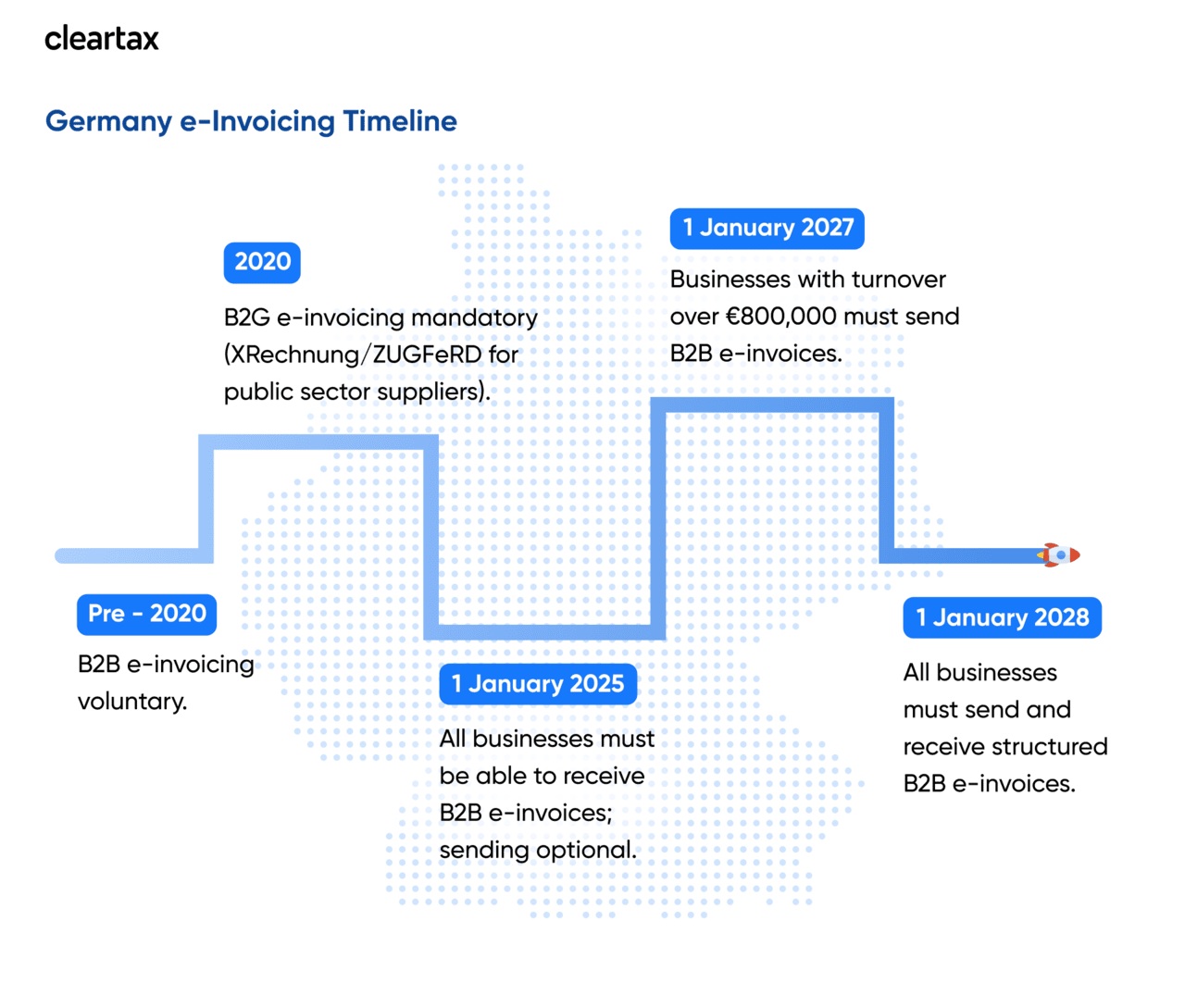
- All businesses must be able to receive e-invoices from January 2025, issuing becomes mandatory in phases until universal compliance by 2028.
- Government doesn’t validate, store, or get involved in any part of the e-invoicing process for now.
- e-invoices must be securely archived in their original format for at least 10 years.
- Exemptions apply to B2C transactions, invoices under €250, passenger tickets, and VAT-exempt sales, and inter EU transactions
What is e-Invoicing in Germany?
e-Invoicing, or electronic invoicing, is the process of issuing, sending, receiving, and storing invoices in a structured digital format that enables seamless, automated processing by computers without manual data entry or paper handling.
e-Invoicing in Germany refers to the legal mandate that requires German businesses to use structured digital invoices for business transactions, especially between companies (B2B). E-invoicing is much more than just sending an invoice by email.
It’s about exchanging invoices as structured, machine-readable data that enables automation, compliance, and efficiency now required by law for B2G and B2B transactions in Germany. The German tax authority released the official E-Invoicing Guidelines (in German) on 25 October 2025.
Germany E-Invoicing Timeline and Compliance Deadlines
Germany is transitioning from voluntary electronic invoicing to a phased mandatory e-invoicing system for all B2B transactions. While e-invoicing has been required for business-to-government (B2G) invoices since 2020, the focus is now on B2B e-invoicing.
Who must comply with Germany's e-Invoicing mandate?
The following entities and transactions are subject to Germany’s mandatory e-invoicing obligations:
- All domestic B2B invoices: where both the supplier and the recipient are based in Germany.
- Taxable Supplies under VAT: Any taxable supply of goods or services that fall within the scope of German VAT law (UStG).
- Business-to-Government (B2G) suppliers: Business invoicing to federal and state public administrations.
- Foreign Entities with Local Establishments: Foreign businesses operating in Germany with "fixed establishment" (e.g., a physical office or warehouse)
Who all are exempted from e-invoicing in Germany
The following transactions and entities are excluded from Germany’s mandatory e-invoicing mandate:
- Small-amount invoices with a gross total of €250 or less.
- Passenger transport tickets, which are exempt from structured invoice requirements.
- VAT-exempt transactions as defined by specific provisions in the VAT Act (UStG)
- Foreign businesses without Local establishment: that are only VAT-registered in Germany, but do not have a fixed establishment, are not subject to this mandate.
- Cross-border transactions whether incoming or outgoing.
- Business-to-consumer (B2C) transactions: Sales to private individuals remain outside the scope. Traditional formats such as paper receipts or PDFs can still be used for consumer sales.
E-Invoicing Formats in Germany: XRechnung & ZUGFeRD
EN 16931-compliant formats like XRechnung and ZUGFeRD are the officially accepted electronic invoice formats for public sector transactions and form the basis for the phased B2B e-invoicing mandate. Both formats defines the mandatory data structure and content required for electronic invoices in Germany.
1. XRechnung
- XRechnung is Germany’s official implementation of the European Norm (EN) 16931 standard.
- It is an XML-based format designed to ensure all the essential invoice data can be automatically extracted and validated by recipient systems.
- XRechnung is mandatory for all invoices issued to German public sector authorities (B2G) and will also be the default format for B2B e-invoicing from 2025.
- The specification is maintained by KoSIT (Coordination Office for IT Standards) and is regularly updated to reflect EU and German legal requirements.
- It is not intended to be human-readable; instead, it is processed by software or viewed through specialized tools.
2. ZUGFeRD
- ZUGFeRD (Zentraler User Guide Forum elektronische Rechnung Deutschland) is a hybrid format.
- It combines a human-readable PDF/A-3 document with an embedded XML file that carries structured invoice data.
- The latest ZUGFeRD 2.x profiles are compliant with EN 16931, and the “XRechnung-compatible” profile is accepted for both B2G and (soon) B2B invoices.
- This format is popular because it bridges the gap between fully digital processing and user-friendly readability for accounting staff.
e-Invoicing Framework in Germany
Germany’s e-invoicing framework is built to enable flexible, secure, and interoperable electronic invoice exchanges across both the private and public sectors.
- Decentralized Exchange: Unlike some countries, Germany does not require B2B invoices to pass through a central government portal (clearance model). Instead, invoices are exchanged directly between businesses, using email, EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), or networks like Peppol.
- Public Sector (B2G) Portals: For invoicing public entities, suppliers must use official portals such as the E-Rechnungsportal Bund or OZG-RE at the federal level, or state-specific platforms. These are Peppol-enabled and accept XRechnung and compatible ZUGFeRD files.
- Post-Audit Model: Germany uses a post-audit model for e-invoicing, meaning tax authorities may request invoices for audit after the fact but do not automatically receive all invoices in real time.
e-Invoicing Process in Germany
Electronic invoice exchange in Germany relies on structured data, compliance with legal standards, and digital automation.
- Invoice Generation: Businesses create e-invoices using ERP, accounting software, or an e-invoicing solution provider. These providers ensure invoices are formatted as XRechnung (XML) or ZUGFeRD (PDF/A-3 + XML) and contain all required data for VAT compliance.
- Transmission: Invoices are sent directly to trading partners via email, EDI, Peppol network, or service provider platforms. The exchange channel is chosen by agreement, but the invoice must remain in a structured format.
- Receipt and Validation: The recipient’s software or e-invoicing provider validates the invoice for format and data integrity. Valid e-invoices are automatically processed into ERP or accounting systems.
- Archiving: All e-invoices must be archived in their original electronic format for 10 years, ensuring authenticity, integrity, and legal audit-readiness.
Note: Invoices to government bodies are submitted through official portals (E-Rechnungsportal Bund, OZG-RE, or state platforms). E-invoicing solution providers can automate submission, integrate with these portals, and validate file compliance.
How Businesses Should Transition to E-Invoicing in Germany: Step by Step Guide
Transitioning to e-invoicing is now a strategic necessity in Germany due to new legal mandates and the need for digital efficiency. Companies must ensure compliance while improving invoice accuracy, speed, and traceability.
Step 1: Map Current Invoice Flows:
Document how invoices are created, approved, sent, received, and archived. Identify gaps in digitalization and pinpoint manual bottlenecks.
Step 2: Understand Compliance Requirements
Review which transactions require e-invoicing (B2B, B2G), applicable formats (XRechnung, ZUGFeRD), and upcoming deadlines based on company size and turnover.
Step 3: Upgrade IT Infrastructure
Ensure your ERP or accounting software supports structured e-invoice formats. Evaluate whether existing systems require integration modules or a switch to more advanced platforms.
Step 4: Select the Right E-Invoicing Provider
Compare features, compliance coverage, integration options, and user support among solution providers. Look for certified Peppol access and automatic format validation.
Step 5: Establish Internal Policies
Develop standard operating procedures for issuing, receiving, and archiving e-invoices. Define roles, responsibilities, and escalation paths for invoice exceptions or errors.
Step 6: Train Employees and Communicate Externally
Provide targeted training for accounting, IT, and operations staff. Inform business partners of your new e-invoicing capabilities and preferred exchange channels.
Step 7: Test Thoroughly Before Going Live
Pilot e-invoicing with selected suppliers and customers to ensure interoperability, error handling, and seamless workflow integration.
Step 8: Monitor Regulatory Changes
Regularly review government updates and solution provider communications to stay ahead of evolving legal and technical requirements.
How Germany’s e-Invoicing Differs
Germany’s e-invoicing approach contrasts with other European countries like Poland and France e-Invoicing mandate, especially in terms of centralization, clearance requirements, and transmission models. The following table outlines the main differences:
Feature | Germany | France | Poland |
Model | Decentralized, post-audit | Centralized clearance (real-time to govt) | Centralized clearance (real-time to govt) |
Format | XRechnung (XML), ZUGFeRD (PDF/XML) | Factur-X (EN 16931, PDF/XML hybrid), XML | KSeF XML (custom Polish format) |
Transmission | Direct, Peppol, or public sector portal | All invoices routed via Chorus Pro (central portal) | All invoices routed via KSeF (central platform) |
Human-readable | PDF option via ZUGFeRD | PDF/XML hybrid (Factur-X) | XML only; human-readable optional |
Mandate Timeline | B2G: 2020; B2B: 2025–2028 phased | B2G: 2020; B2B: 2026 (phased) | B2B: 2024 (full clearance from July 2024) |
Tax Authority Access | Audit on request | Real-time, automatic copy to tax authority | Real-time, automatic copy to tax authority |
ClearTax E-Invoicing Solution
ClearTax offers a robust e-invoicing platform built for German regulatory needs, providing seamless integration, automation, and centralized management for businesses transitioning to digital invoicing.
- ERP Integration & Middleware: Connects directly with leading ERPs (SAP, Oracle, Dynamics) and acts as middleware for data mapping, enrichment, and validation, ensuring invoices always meet legal standards.
- Centralized Cloud Portal: Enables invoice generation, viewing, archiving, downloading, and real-time tracking, all in one secure dashboard.
- Peppol Accredited: Certified for direct, compliant e-invoice exchange across Germany and the EU public sector.
- Automation & Compliance: Features automatic data validation, regulatory updates, and secure storage for 10 years.
- Scalable & Secure: Cloud-based, multi-entity support, advanced security, and expert onboarding for businesses of any size.
Conclusion
The e-Invocing mandate in Germany applies strictly to B2B transactions where both parties are established in Germany. Public sector entities already require e-invoices since 2020, submitted through official portals like the E-Rechnungsportal Bund or state systems.
Unlike countries with centralized clearance models, Germany follows a decentralized, post-audit approach: invoices are exchanged directly between businesses without real-time tax authority validation.
This model prioritizes interoperability and flexibility while laying the foundation for potential future EU-wide real-time reporting under the VAT in the Digital Age initiative.


